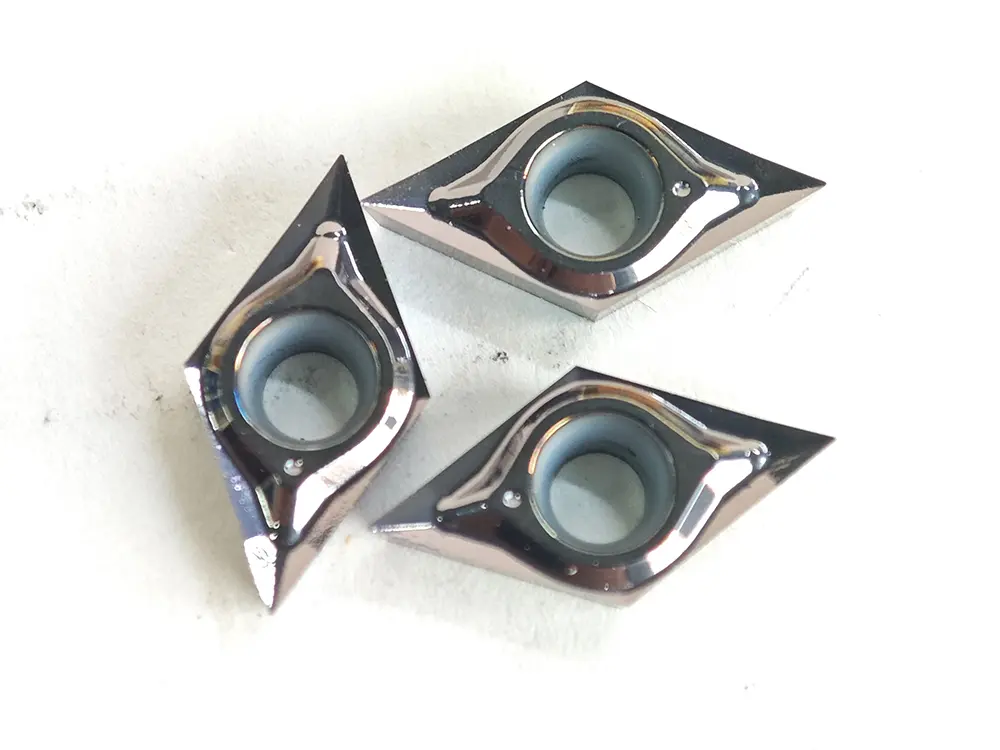
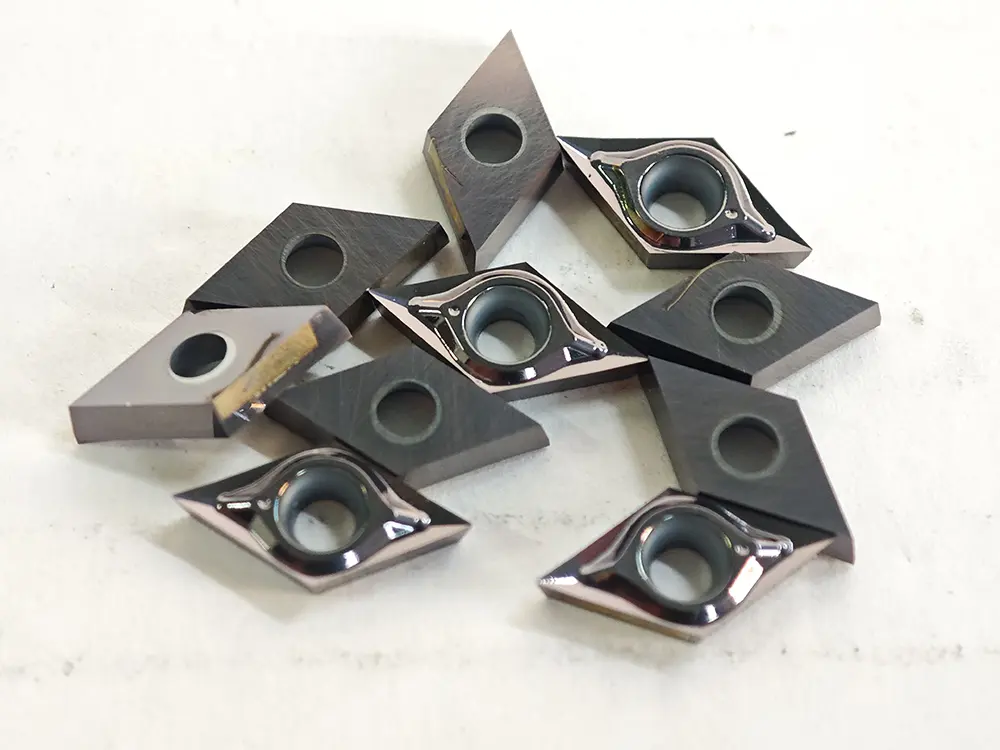
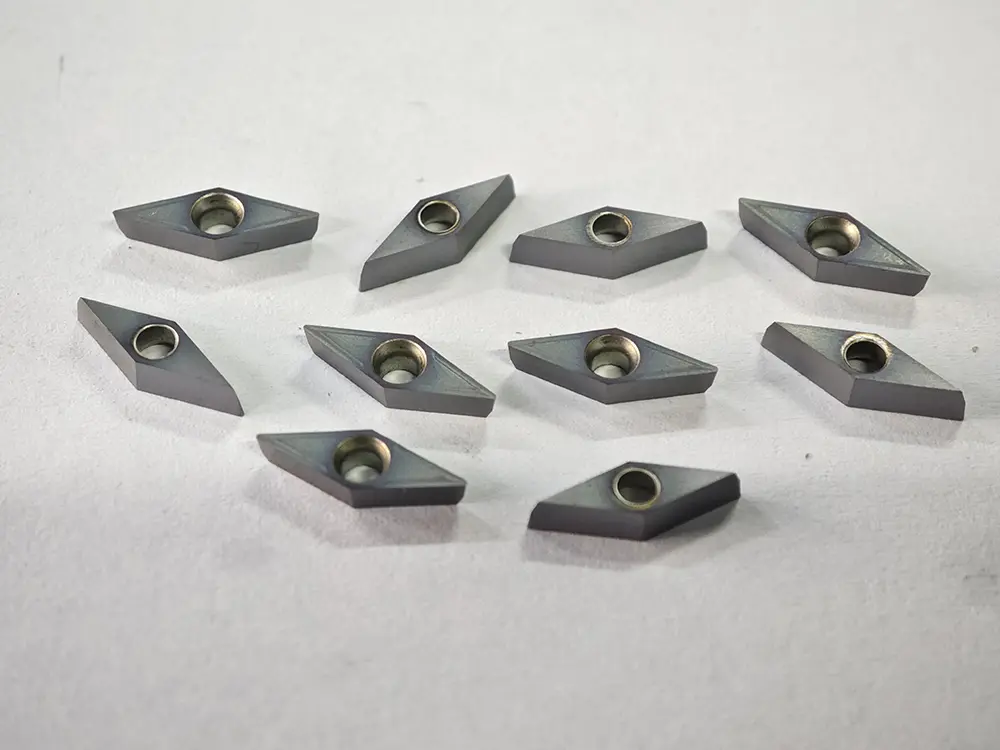
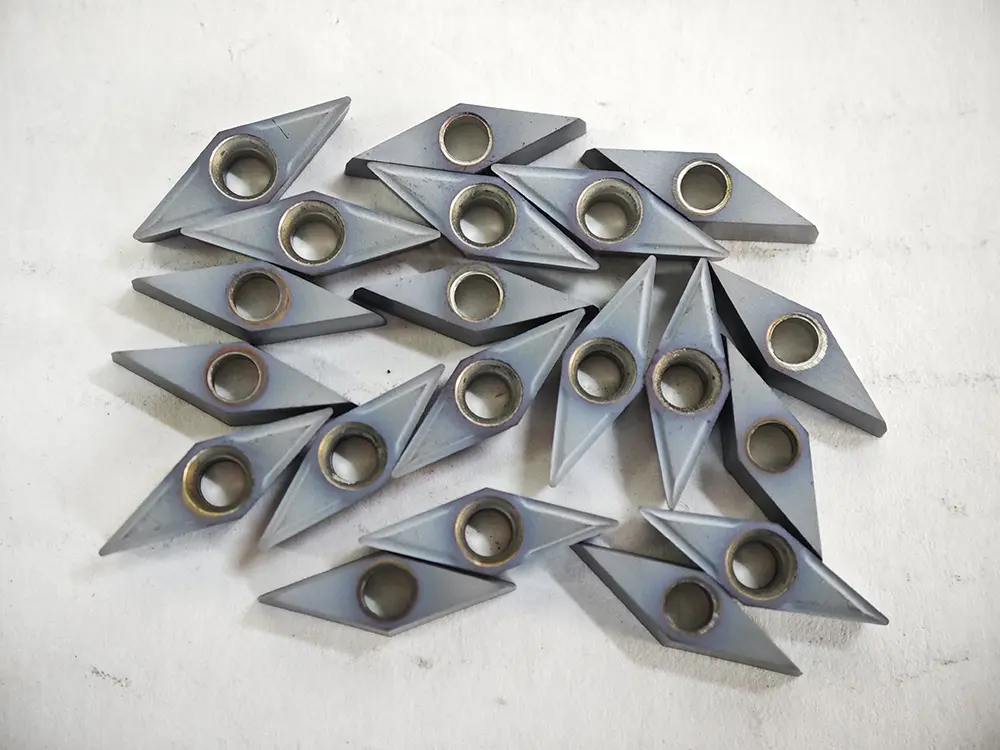
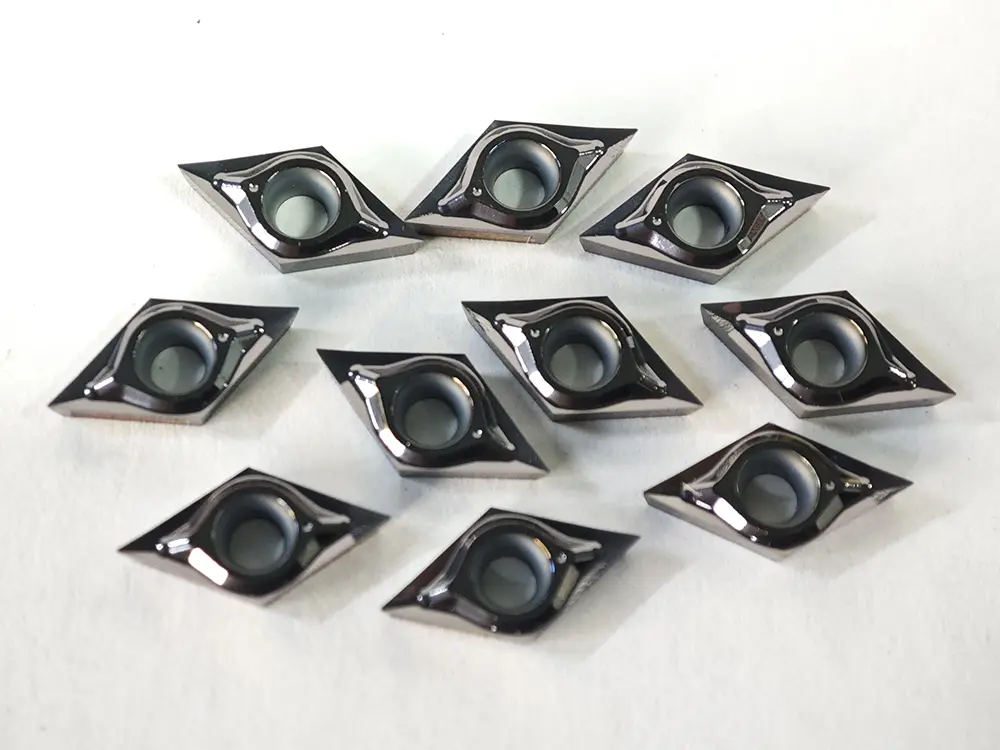
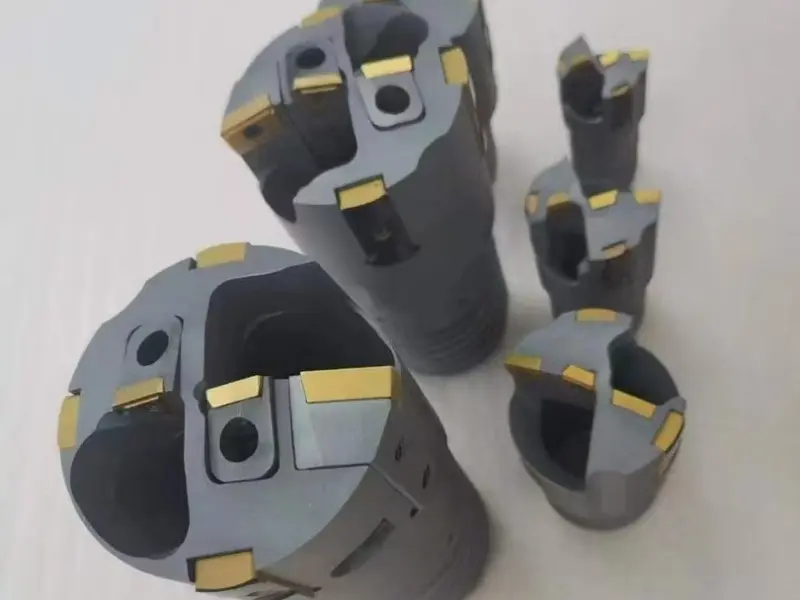
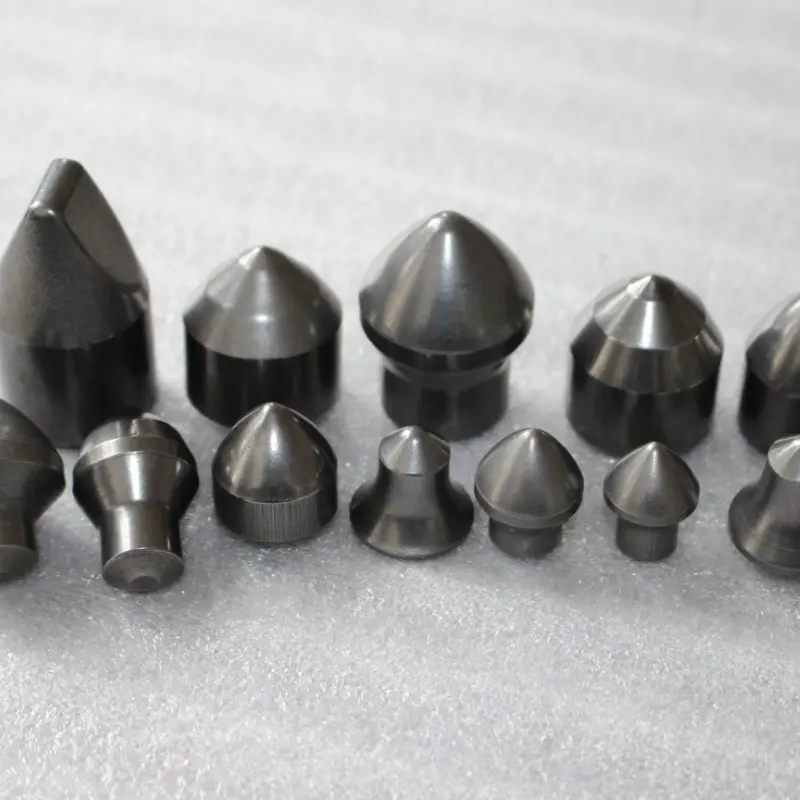
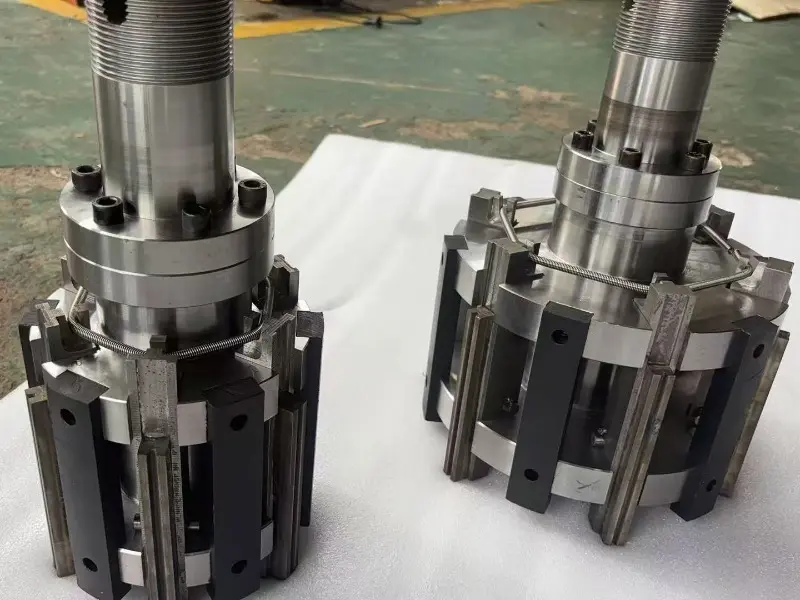
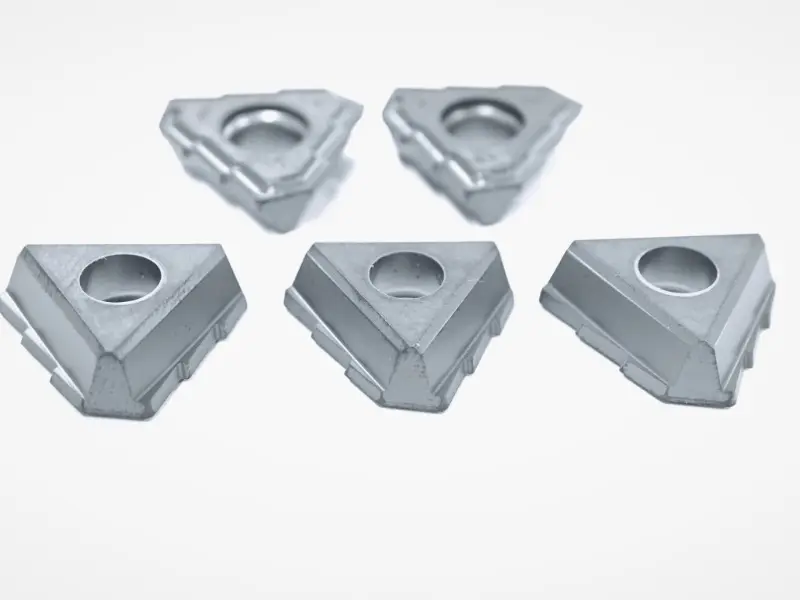
Shape and Angles:
The insert is entirely rhombic, with its core feature being a fixed included angle between two adjacent cutting edges (tool nose angle). Common tool nose angles are 35°, 55°, 60°, and 80°, among which the 80° rhombic insert (e.g., CNMG series) is most widely used. Inserts are designed with double sides (single-sided for some models), each featuring 2–4 usable tool noses. The cutting edges are equipped with chip breaker grooves (general-purpose, finish machining, or rough machining types), and the bottom is provided with positioning holes or positioning grooves (compatible with tool holder clamping mechanisms).
Cutting Edge Design:
The cutting edge is divided into the main cutting edge (responsible for primary cutting) and the auxiliary cutting edge (responsible for surface finishing of workpieces). Some inserts are with edge chamfers (to enhance cutting edge strength) or passivation treatment (to prevent chipping). The shape of chip breaker grooves is designed according to the machined material (e.g., wide chip breaker grooves for steel workpieces, narrow ones for cast iron).
Positioning Structure:
The mainstream adopts circular hole positioning (central hole clamping) or counterbore positioning (lever clamping), with a positioning accuracy of ±0.005mm and radial runout ≤0.01mm after clamping, ensuring consistency in machining dimensions.